Introduction
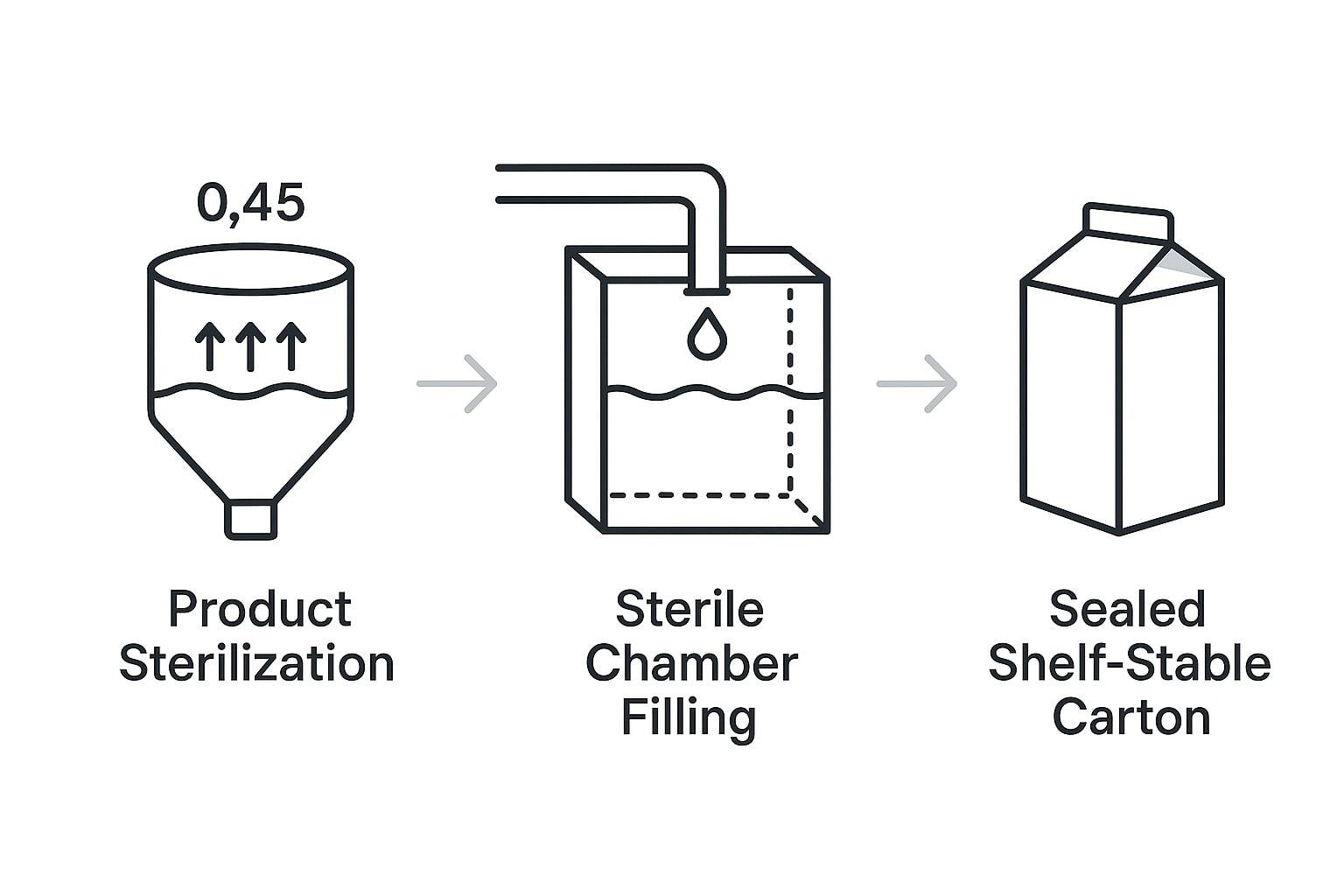
Aseptic packaging is a breakthrough in food and beverage preservation, offering long shelf life without refrigeration. Unlike traditional methods that rely on preservatives or cold storage, aseptic systems sterilize the product, packaging, and environment—then seal to lock in freshness and safety. This guide explains how aseptic packaging works and why it’s one of the most efficient systems in modern manufacturing.