Introduction
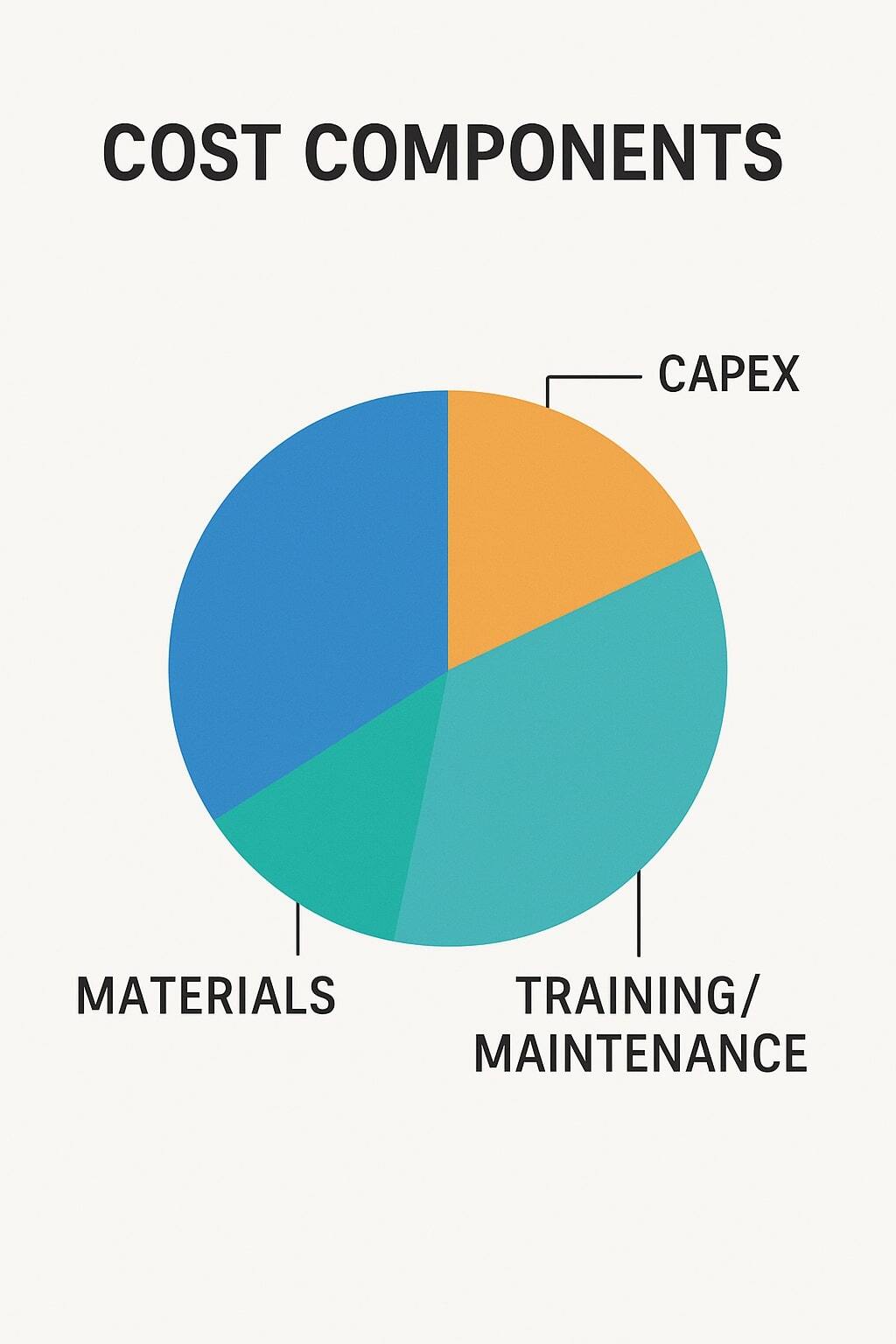
Aseptic packaging delivers long shelf life, product safety, and global distribution advantages. However, it comes with challenges that brands must prepare for. From upfront costs to technical expertise, the risks should be understood before investing. For a complete overview of process and benefits, see the step-by-step aseptic guide.